1、 Type, function, model, structure and use characteristics of cable sheath
1、 Classification of cable sheath
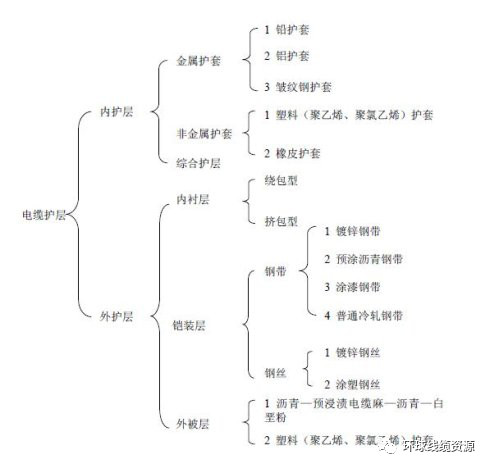
Cable The sheath can generally be divided into inner sheath and outer sheath. The sheath tightly wrapped on the cable insulation layer is called the inner sheath, and the cover outside the inner sheath is called the outer sheath.
2、 Function of cable sheath
The outer sheath is mainly composed of inner liner, armor layer and outer sheath.
( 1) Inner liner
Function: in the process of armoring, prevent the inner protective layer from being damaged by the armoring layer; During laying and operation, it can resist the invasion of external corrosive media, prevent the metal sheath (inner sheath) from contacting with external corrosive media, and extend the service life of the cable.
( 2) Armor layer
Function: prevent the cable from possible mechanical damage during laying or operation, so as to ensure the integrity of the inner sheath and bear certain external force.
( 3) Exodermis
Function: mainly to protect the armor layer and prevent the armor layer from being damaged during laying. The outer coating composed of plastic sheath can prevent the armor layer from being corroded during operation.
Cable The sheath is to ensure that the cable can maintain excellent electrical performance for a long time. Once the sheath is damaged, the cable will fail and cannot continue to operate. Therefore, the service life of the cable largely depends on the service life of the cable sheath, and the service life of the surface cable sheath largely depends on the manufacturing quality of the sheath.
3. Structure of various protective layers
( 1) Metal sheath general cable outer sheath structure
( 2) Structure of general cable sheath with non-metallic sheath
( 3) Outer sheath structure of lead sheathed oil filled cable
( 4) Steel pipe cable sheath
surface 1 Structure of general cable sheath with non-metallic sheath
model | Outer sheath structure |
Inner liner | Armor layer | Exodermis |
twelve | Wrapping type: plastic tape or non-woven fabric Extrusion type: plastic sleeve | Interlocking armor | PVC jacket |
twenty-two | Double steel tape armouring | PVC jacket |
twenty-three | Polyethylene jacket |
thirty-two | Single round steel wire armouring | PVC jacket |
thirty-three | Polyethylene jacket |
fifty-three | Single corrugated steel strip longitudinally wrapped armor | Polyethylene jacket |
sixty-two | Double aluminum tape (aluminum alloy tape) armouring | PVC jacket |
sixty-three | Polyethylene jacket |
forty-two | Plastic sleeve | Single thick He steel wire armouring | PVC jacket |
forty-three | Polyethylene jacket |
forty-one | Adhesive coating - polypropylene rope -, or cable asphalt - impregnated hemp - cable asphalt - chalk |
four hundred and forty-one | Double thick round steel wire armouring |
two hundred and forty-one | Double steel strip single thick round steel wire armouring |
4. Use of cable sheath
surface 2 Scope of application of general sheath for non-metallic sheathed cables
model | name | Mainly applicable to laying places |
Laying method | Special environment |
indoor | Tunnel | Cable trench | The Conduit | underground | Shaft | Underwater | inflammable | Severe corrosion | pull |
General soil | Gravelly |
twelve | Interlocking steel belt armored PVC jacket | △ | △ | △ |
| △ | △ |
|
| △ | △ |
|
twenty-two | Steel tape armored PVC jacket | △ | △ | △ |
| △ | △ |
|
| △ | △ |
|
twenty-three | Steel tape armored polyethylene jacket | △ |
| △ |
| △ | △ |
|
|
| △ |
|
thirty-two | Fine round steel wire armored PVC jacket |
|
|
|
| △ | △ | △ | △ | △ | △ | △ |
thirty-three | Fine round steel wire armored polyethylene jacket |
|
|
|
| △ | △ | △ | △ |
| △ | △ |
forty-one | Thick round steel wire armored fiber sheath |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| △ |
| ○ | △ |
forty-two | Thick round steel wire armored PVC jacket |
|
|
|
|
|
| △ | △ | △ | △ | △ |
forty-three | Thick round steel wire armored polyethylene jacket |
|
|
|
|
|
| △ | △ |
| △ | △ |
sixty-two | Aluminum tape armored PVC jacket | △ | △ | △ |
| △ | △ |
|
| △ | △ |
|
sixty-three | Aluminum tape armored polyethylene jacket | △ |
| △ |
| △ | △ |
|
|
| △ |
|
four hundred and forty-one | Double thick round steel wire armored fiber sheath |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| △ |
| ○ | △ |
two hundred and forty-one | Steel belt - thick round steel wire armored fiber sheath |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| △ |
| ○ | △ |
2、 Common materials for cable sheath
There are basically four types of materials commonly used for cable sheath: fiber materials, metal materials and plastics.
1、 Fibrous material
( 1) Paper: cut from 0.12mm thick cable paper.
( 2) Hemp: Cable hemp made from jute.
2、 Metallic materials
The metal materials used in the outer sheath are mainly steel strip, steel wire, aluminum strip (aluminum alloy strip), etc.
( 1) Steel strip
The steel strip includes cold rolled steel strip, painted steel strip and galvanized steel strip.
1) Cold rolled steel strip
It is made of hot rolled steel strip by cold rolling, mainly used for processing Cable For painted steel strip and galvanized steel strip of armor layer.
surface 3 Dimension and allowable deviation of cold rolled steel strip for armored cable
Thickness mm | Allowable deviation mm | Width mm | Allowable deviation mm |
zero point two zero | ±0.02 | 10,15,20,25 | ±0.50 |
zero point three zero | ±0.03 |
zero point five zero | ±0.04 | 30,35 | ±1.00 |
zero point eight zero | ±0.05 | 40,45 | ±1.50 |
one | ±0.06 | 50,55,60 | ±2.00 |
2) Painted steel strip
It is made of paint film formed on cold rolled steel strip by dip coating method or electrophoresis method. The specifications and dimensions are the same as those of cold rolled steel strip.
The tensile strength of painted steel strip shall not be less than 300N/mm two , elongation shall not be less than 20%。
The film quality of painted steel strip shall comply with Table 4.
surface 4 Paint film quality of painted steel strip
Project | Indicators |
appearance | Even and continuous, slight sagging and scratches are allowed, but there shall be no large areas of falling off or missing coating |
Thickness (single side) ≥ μ m | eight |
Bending test (Φ 5mm)/time | one |
impact test (once)/N · cm | Steel strip thickness < 0.5mm ≥ | one hundred |
Steel strip thickness ≥ 0.5mm ≥ | three hundred |
Corrosion resistance test 20℃±5℃,24h | 5% hydrochloric acid solution | The paint film is complete, and it is allowed to peel off no more than 30% of the total area of the sample. Small bubbles on the surface are not counted |
5% sodium hydroxide solution | The paint film is complete, and the paint film on the cutting edge is allowed to have a slight peeling of no more than 5mm. |
5% sodium chloride solution |
Heat resistance test 200 ℃± 5 ℃, 0.5h, Φ 5mm bending once | No crack, and the allowable film crack within 3mm from the edge can be ignored |
Low temperature resistance test - 20 ℃± 5 ℃, 2h, Φ 5mm bending once |
3) Galvanized steel strip
Galvanized steel strip is made of cold rolled steel strip coated with zinc. The methods are hot plating (R) and electroplating (D).
The specifications, dimensions and mechanical properties of the steel strip are the same as those of the cold rolled steel strip.
The galvanized layer of steel strip shall be uniform and complete, free of zinc layer peeling, cracks, rust and missing plating, but some defects such as missing plating points are allowed. See Table 5 for zinc coating weight of galvanized steel strip.
surface 5 Weight of zinc layer of galvanized steel tape for armored cable
Symbol | Average value of three-point test (g/m two )≥ | Minimum value of three-point test (g/m two )≥ |
R200 R275 R350 D80 | two hundred two hundred and seventy-five three hundred and fifty eighty | one hundred and seventy two hundred and thirty three hundred sixty-eight |
( 2) Steel wire
Galvanized steel wire for armouring is made of hot-rolled low carbon steel wire rod.
See Table 6 for specifications and dimensions of galvanized steel wire for armored cable.
surface 6 Specifications and dimensions of galvanized steel wire for armouring
Nominal diameter mm | Allowable deviation mm |
one point six 2.0 2.5 3.15 4.0 5.0 6.0 | ±0.05 ±0.08 ±0.10 ±0.13 |
See Table 7 for the quality of zinc coating of galvanized steel wire for armored cable.
surface 7 Quality of zinc coating on galvanized steel wire for armored cable
Wire diameter mm | Weight of zinc layer (g/m) two | Number of immersion in copper sulfate solution (once every 60s) ≥ | Winding test |
Mandrel diameter is multiple of steel wire diameter | Winding times ≥ |
one point six two two point five three point one five four five six | one hundred and fifty one hundred and ninety two hundred and ten two hundred and forty two hundred and seventy two hundred and seventy two hundred and seventy | two two two three three three three | four four four four five five five | six |
The surface of galvanized steel wire tested with copper sulfate solution shall be free of bright metallic copper that cannot be wiped off with cotton or clean cloth; After winding test, the zinc layer shall not break or delaminate.
The galvanized layer shall be even and free from cracks, spots and places without galvanizing. Individual zinc layer accumulation is allowed, but the value that increases the steel wire shall not exceed 15 times the diameter tolerance.
To ensure the mechanical strength of the steel wire, the bundled or coiled steel wire shall be composed of one piece, without broken ends and galvanized electrical joints, and the bundled steel wire shall not be wound too tightly or bent.
3 Plastic
Polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride.
three Armoring process
1 Preparation before armoring
Before cable armoring, first check the semi-finished product responsibility card according to the planned work order, and measure and check the semi-finished product specification, cable outer diameter, surface quality, etc. Any semi-finished product that does not meet the requirements can not be processed, and then adjust the steel belt and select the mold according to the process specification according to the model on the semi-finished product responsibility card. The diameter of mold hole is 1~4mm larger than that of cable core.
2 Quality requirements and operation process of armoring
( 1) Quality of steel strip wrapping
The wrapping type inner liner shall be smooth to eliminate overlap, otherwise the cable diameter will be uneven.
The two layers of steel strips are wound with gaps, and the direction of wrapping is right. The wrapping should be tight and flat. The overlap of the upper and lower layers of steel strips should not be less than 1/4, the clearance is generally 1/3 of the width of the steel strip used.
See the table for selection of steel strip specifications 8。
surface 8 Nominal thickness of armored metal tape
Assumed diameter before armoring mm | Nominal thickness of metal strip mm |
Steel strip or galvanized steel strip | Aluminium or aluminium alloy strip |
d≤30 30<d≤70 70<d | zero point two zero point five zero point eight | zero point five zero point five zero point eight |
The tension adjustment of the steel belt wrapping head is an important operation of the armor. Even tension is the key to ensure the quality of the armor. It is required that the tension of the two steel belt reels be even and consistent, otherwise the cable core will swing, and the cable core will be cut in serious cases. It is required that the tension of the steel belt is consistent from beginning to end, or there will be structural deformation and uneven outer diameter.
The steel strip joint shall be flat and firm, and the edge of the joint shall be free of burrs, sharp corners, etc. The steel strip shall be rewound tightly, and the steel strip with interlayer, burr, sand hole and rust defect shall be removed during rewinding.
( 2) Steel wire wrapping quality
The steel wire wrapping must be arranged closely and neatly, without jumper, overlap, and clearance greater than the diameter of one steel wire. If there is a steel wire bulge or clearance greater than the diameter of one steel wire, the steel wire wrapping pitch can be adjusted.
The steel wire wrapping pitch shall be 7~12 times, the wrapping direction is left.
The steel wire joint shall be flat and firm, and the welding position shall be repeatedly bent and inspected to prevent faulty welding. If there is burr or protruding sharp corner at the welding position, it must be filed flat. The tension of the wire reel shall be checked at any time, and the tension of each reel shall be uniform without any over tightening or over loosening.
The steel wire shall be rewound tightly, and the wire arrangement shall be flush. No single sided or drum shaped wire reel is allowed. The wire reel used for rewinding shall be a flat and intact iron reel to prevent scratching the zinc layer of the steel wire during rewinding.
See the table for selection of steel wire specifications 9。
surface 9 Selection of steel wire specifications
Assumed diameter before armoring mm | Diameter of fine steel wire mm | Diameter of coarse steel wire mm |
15.0≤d 15.0<d≤25.0 25.0<d≤35.0 35.0<d≤60.0 60.0<d | 0.8~1.6 1.6~2.0 2.0~2.5 2.5~3.15 three point one five | 4.0~6.0 |
four Types and causes of defective products
1 Steel strip defect
The defects of steel strip wrapping mainly include the following:
1) The inner lining layer is damaged due to the curling and cracking of the steel belt, the inconsistent tension of the two steel belt reels and the swaying of the cable core, the excessive tension of the two steel belt reels and the poor welding of the steel belt with sharp corners;
2) The steel strip gap exceeds the standard, which is caused by the mismatch of pitch gears, too narrow steel strip width, the actual outer diameter of the cable exceeds the standard, and the asynchronous take-up and traction, which causes the steel strip gap of the cable to start;
3) The reason for the steel belt missing is that the tension of the steel belt is not adjusted properly Cable The mold is too large and the wrapping angle of the steel strip is inappropriate; 4) The overlap rate of steel strip is too large, which is caused by too large steel strip width, too small cable outer diameter, and too small traction speed.
2 Steel wire defects
The defects of steel wire armoring mainly include the following:
1) The inner liner is damaged due to poor steel wire joints and damaged inner liner;
2) Steel wire jumpers, bulges and gaps are caused by uneven arrangement and tension of steel wires Poor control, bent steel wire, uneven cable outer diameter;
3) The zinc layer of steel wire is scraped off, which is caused by grooves in the junction plate, threading die, threading hole, etc., and the parallel die is too small 。




